Improve network range and stability
In case you are experiencing an unstable or bad network range you can do the following things to improve your network.
Adapter
Use a recommended adapter, especially the CC2530 and CC2531 are known to perform poorly.
Avoid devices from AwoX
It is known that AwoX devices cause network issues. In case you are having issues, remove them from your network. It may help to OTA update your device via the "AwoX HomeControl" app over Bluetooth.
USB based adapter
The range of these adapters can greatly be improved when connecting them with an USB extension cable instead of directly plugging it into the computer (e.g. Raspberry Pi). When plugged directly into the computer, the antenna suffers from interference of radio signals and electrical components of the computer. Also be sure not to position the adapter too close to any other radio transmitting devices (e.g. a Wi-Fi router) or an SSD.
A USB extension cable of 50 cm is already enough to reduce the interference. Preferably get one with shielding as this may give better results (source).
Do not underestimate this! Placing your adapter close to an USB or HDMI port can kill the radio signal entirely as demonstrated in this article.
Additionally, it may help to plug the adapter to a USB 2 instead of USB 3 port.
Try different orientations of the adapter
RF connection between the adapter and other devices also depends on the way it is oriented in space. You might be having very poor linkquality reports and intermittent ping failures but once the adapter is rotated a little it all can change greatly without re-locating the coordinator far away. Try to experiment with positioning and orienting the adapter in space while monitoring the linkquality values reported. You might find it useful to buy a small rotating USB connector like this:

Reduce Wi-Fi interference by changing the Zigbee channel
Changing the Zigbee channel might require re-pairing some of your devices, read the documentation for more info
As Wi-Fi and Zigbee both operate on the same frequency space (2.4 GHz), they can interfere with each other. By using the correct Zigbee channel, interference with Wi-Fi can (partly) be avoided. A good article explaining this is Zigbee and Wi-Fi Coexistence.
To change the Zigbee channel Zigbee2MQTT uses you have to set the channel in configuration.yaml.
Interference from other 2.4 GHz devices
Any device using the open 2.4 GHz spectrum could interfere with Zigbee such as Bluetooth or gaming devices like Logitech “Unifying” or “Lightspeed” or Razer “Hyperspeed Wireless”.
This includes devices that you may not realize are 2.4 GHz. Check anything that is wireless including wireless audio transmitters such as:
Utility companies are known to use Zigbee with their "smart meters" but may not advertise them as Zigbee. Other devices that broadcast Zigbee, or modified versions of Zigbee are known to cause issues. For example If you are still using a Philips Hue Hub it is suggested to add the bulbs to your Zigbee2MQTT network or make sure they are on different channels.
Adding routers to your network
"Zigbee is a low-power wireless mesh network standard targeted at battery-powered devices" (see Wikipedia). Yet, low transmission power can be the cause of an unstable or unreliable network:
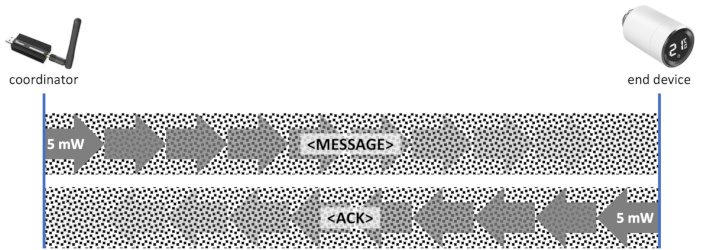
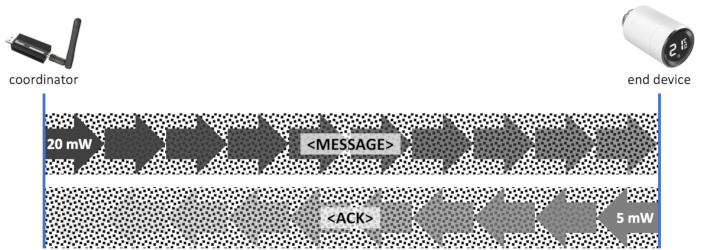
Zigbee2MQTT enables the user to increase the transmission power for some coordinator models. However, this simple measure might yield to a network with weird behavior, if messages to an end device reach their target, but responses (or messages) from that end device do not reliably reach the coordinator:
Introducing a router (read more about this) can improve the forward path as well as the return path:
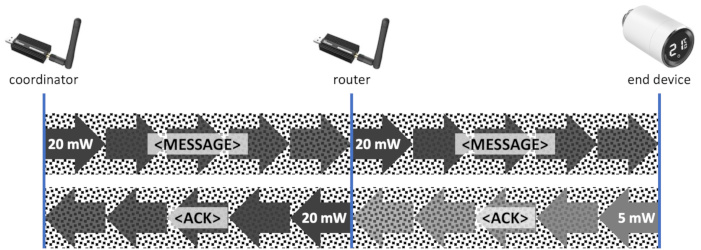
You might choose a dedicated router (for example, a SONOFF ZBDongle-E based router) or a mains-powered Zigbee device (for example, a Hue lamp) to stabilize your network. Almost all AC powered devices will serve as a router (exceptions are most AC powered relays that do not require a neutral wire).
Please note that there are routers of mediocre quality that might not harmonize well with your network (for example, some versions of the SONOFF Smart Plug S26R2ZB are known to be limited). This may yield in message routing errors. In case you have such devices in your network, it might help to add additional routers of better quality and bind your devices to these routers (re-pairing devices with “Permit join” restricted to the new/better router) to improve the overall network performance.
If you assume to have routing problems, try sending an MQTT request to the bridge to the topic zigbee2mqtt/bridge/request/networkmap to retrieve a map of your Zigbee network including routes.
For more technical details on Zigbee routing, see the "5. Routing" in the TI Z-Stack User Guide, for example.
Hardware
Although Zigbee2MQTT does not require many resources, the hardware you are running Zigbee2MQTT on can impact the performance. This is especially true when using low-power hardware like the Raspberry Pi 3. Make sure that enough resources (CPU/memory) is free. For example, running Home Assistant + Zigbee2MQTT Home Assistant addon on the Raspberry Pi 3 may give bad performance.
Broadcasts
Zigbee traffic can be categorized as either Unicast or Broadcast:
- Unicast is an addressed message, usually between a Zigbee device and the coordinator, possibly through some intermediate devices
- Broadcast is a special type of message that is designed to reach all devices in the network
When a device receives a broadcast message for the first time, it will re-transmit it at least once. The device keeps track of broadcasts that have recently been re-transmitted to prevent repeating messages forever. For large networks, broadcasts can generate a lot of traffic, and it takes time for the message to propagate to all devices.
Zigbee can only sustain an average rate of 1 broadcast per second, and multiple broadcasts within a short timespan increases latency. For more information, see this application note by Silicon Labs.
Broadcasts are mostly used for network management tasks such as finding routes to devices, but also by Zigbee Groups and Green Power devices. It is generally recommended to use broadcasts sparingly.
